Abstract
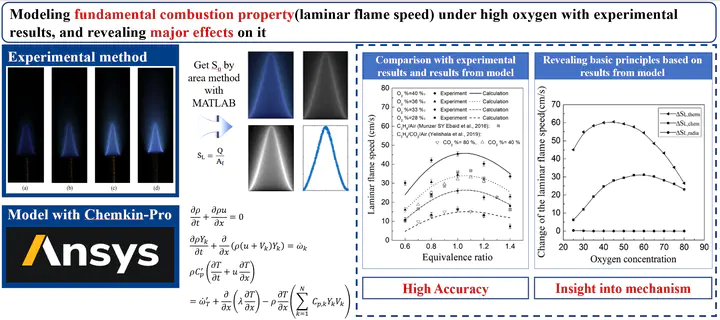
In this paper, the laminar flame speeds of in atmosphere were investigated experimentally and numerically. The laminar flame speeds of C3H8/O2/CO2 were measured using a Bunsen flame under the condition of different equivalent ratios and concentrations at ordinary pressure and temperature. It was found that the laminar flame speed gradually increased with the increase of concentration. The equivalent ratio of the highest laminar flame speed is between 1.0 and 1.1 under each fixed oxygen concentration. The high concentration reduces the laminar flame propagation velocity of , which is due to thermal, radiative and chemical properties of . The calculations were performed to investigate the effects of on the laminar flame speed. Results show that the thermal effect of is the determining factor, the chemical effect is the second factor and radiative effect is the last one. Reaction is the most important chain reaction for the oxidation of C3H8. In addition to this, the third body effect in reaction changed the laminar flame speed significantly in the condition of very low equivalent ratio and concentration.

Computation, Modelling, and Reconstruction
 Abstract
Abstract Abstract
Abstract