 Abstract
AbstractAbstract
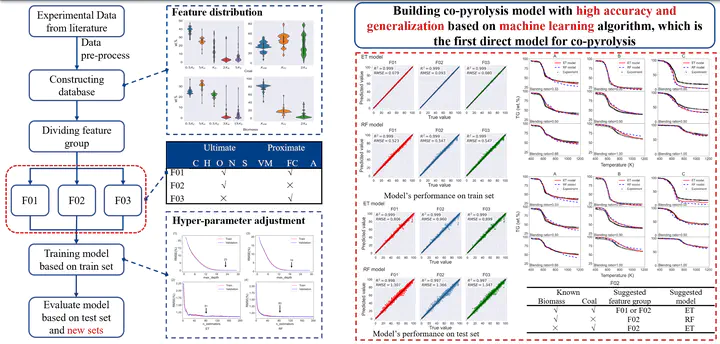
Coal and biomass co-thermochemical conversion has caught significant attentions, in which the co-pyrolysis is always the primary process. The traditional pyrolysis kinetic models are developed individually for coal and biomass, in which the synergistic effect wasn’t comprehensively considered. In the present study, we innovatively explored a new method to accurately model this process using machine learning approaches, specifically the random forest algorithm based on classification and regression trees and extremely trees. First, a co-pyrolyssis database is constructed from experimental data in published literatures, then divided into several sub-sets for training, application, and optimization, respectively. The machine learning models are trained on the training data-set, tested on the test data-set, and applicated on the new data-set. The training and test results demonstrate both models are able to well predict the co-pyrolysis (